

If you want to send bulk email from an email client or set up transactional emails on your website, you’ve probably come across the term SMTP. But you might be wondering, what is SMTP and how does it concern me?
SMTP is quite a technical subject and if you’re new to the world of email, can be a tough one to get your head around.
This guide will give you the SMTP information you need to manage your emails in a way that best serves your business.
We’ll also be looking at how Sendinblue functions as an SMTP server and how you can test-drive our free SMTP server.
Table of Contents
What is SMTP?
SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol) is a communication protocol, or set of rules, used to send email from an email client or webmail provider to a recipient’s email server.
In short, SMTP sends email to its destination. You can think of it as a postal worker picking up mail from your home, finding the correct destination route, then delivering it to the recipient mailbox.
Once transferred to the recipient’s server by SMTP, the email is retrieved using POP and IMAP protocols.

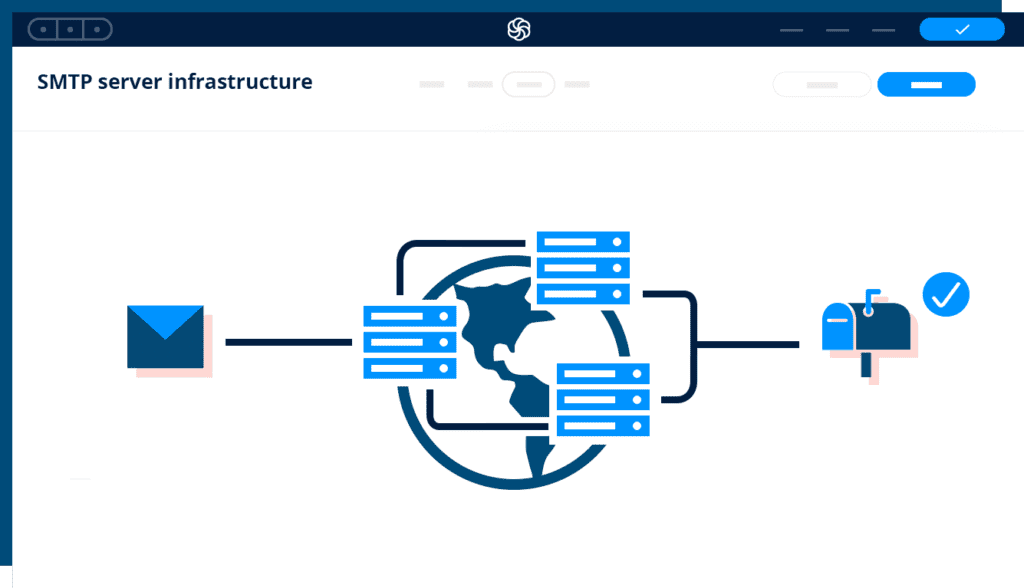
How SMTP email works (for those who really want to know)
As mentioned, SMTP primarily refers to the set of rules that email servers use to transfer emails over the internet from one email server to another.
The protocol works like this:
- The sender and recipient of the message are specified
- A request is sent to both the sender and recipient to verify they exist
- The message is transferred from the sender to the recipient
Steps for transferring messages over the internet according to SMTP
As a marketer, you may not be interested in the minute details of how SMTP works in practice. In that case, feel free to jump ahead.
But if you are interested in the technical side, we’re about to take a more detailed look at the process. First, let’s run through some of the terminology related to SMTP.
Acronyms related to SMTP:
- MUA (Mail User Agent) – Email client (e.g. Gmail, Yahoo, Outlook)
- MSA (Mail Submission Agent) – Computer software run on an SMTP server that receives messages from a MUA and checks for any errors before transferring to a MTA.
- MTA (Mail Transfer Agent) – Software that checks recipient domain’s MX record to decide how to continue transferring the message (either to another MTA, or an MDA)
- MX Record (Mail Exchanger Record) – Is a resource record that specifies from which server the recipient MUA for that domain can retrieve the message.
- MDA (Mail Delivery Agent) – Software that stores messages for batch retrieval for MUAs
Ok, now that you’ve got the SMTP vocabulary down, let’s see how it all fits together to create the protocol for transferring electronic messages over the internet.
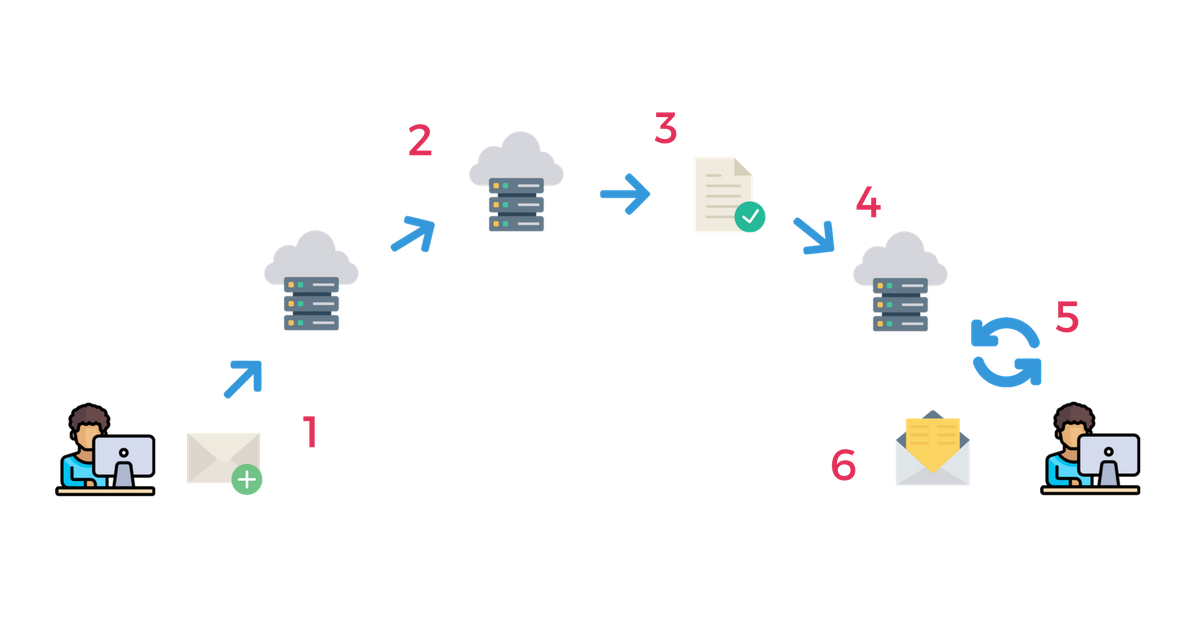
Here are the 6 main steps that comprise the electronic message data transfer process for SMTP:
- Email is submitted by a MUA to a mail server’s MSA
- The message is transferred to the server’s MTA (the MTA and MSA are usually hosted on the same SMTP server)
- The MTA checks the MX record of the recipient domain and transfers the message to another MTA (this step can occur multiple times until the message is received by the proper receiving server)
- The message is handed off to the MDA, which saves messages in the proper format for retrieval by the receiving MUA
- The receiving MUA requests the message from the MDA (usually with POP3 or IMAP)
- The message is delivered to the receiving MUA‘s inbox
To give you a clearer visual, here’s a graphic that shows the process in action:

What is an SMTP server?
Any server that receives, handles, transfers, or stores electronic messages transferred through SMTP can be considered an SMTP server.
There are two types of SMTP server you’ll come across:
- ‘Regular’ SMTP servers for sending everyday personal email. These servers typically belong to email providers like Gmail, Internet Service Providers like AT&T, or web hosting providers like Bluehost. They usually have strict daily sending limits.
- Dedicated SMTP relay servers for sending bulk email and transactional emails. Companies like Sendinblue have dedicated servers that support high-volume sending for their customers.
What is an SMTP Relay?
SMTP Relay refers to the actual SMTP servers through which emails pass before arriving at their destination. But no need to get into the specifics, just think of it as a synonym for SMTP server.
Where is the SMTP server located?
If you’re wondering where to find your SMTP server address, it’ll be in the SMTP settings of your email client or webmail provider.
These settings tell the email client or webmail provider where they need to send an email to.
Each SMTP server has its own SMTP email address or server name. For example, the Gmail SMTP server address is smtp.gmail.com and the Sendinblue SMTP address is smtp.relay.sendinblue.com.
Reminder: The difference between an email client and a webmail provider
Email clients and webmail providers are two methods of sending, receiving, and storing emails.
An email client is an application installed locally on a computer or mobile device that interacts with an email provider’s server using SMTP. When you set up a email client, you need to enter your email provider’s incoming and outgoing mail server settings.
Once the client retrieves your email, it’s stored locally so you can read and access it whenever you want — even when you’re not online. Popular email clients include Microsoft Outlook, Apple Mail, and Mozilla Thunderbird.
A webmail provider (like Gmail, Yahoo, or Hotmail) lets you access email directly on the webmail provider’s server. For example, you connect to the internet and log into your Gmail account to be able to read or send email.
Incoming and outgoing mail is sent over the webmail provider’s servers but these settings can be customized, as we’re about to see next.
Changing the SMTP settings to your email provider of choice
Here’s a key point to note: SMTP server settings can be changed according to the email provider you want to use.
For example if you want to send bulk email through an email client, website, or other application, you can easily change the existing SMTP setting to Sendinblue SMTP or another bulk email provider.
And there are plenty of reasons why you should do this. Let’s take a look at them now.
When to switch to a dedicated SMTP relay service
To send large volumes of email
In the beginning, you might get by sending transactional emails from your website over the PHP mailer function or a free provider like Gmail.
But as your business grows, you’ll need a more robust SMTP service that can handle larger volumes of email.
Free email providers have strict daily sending limits. Sending too many emails could damage your sender reputation or result in important emails landing in the spam folder.
To send larger amounts of email from your email client or website without running into such issues, it’s best to invest in a professional SMTP service like Sendinblue.
Better email deliverability
The SMTP server you use to send out emails is associated with a specific IP address. This address is directly tied to your deliverability because it’s this address that ISPs use to check your sender reputation.
The shared IPs of free email providers aren’t monitored closely enough. This means you could be sending emails from the same email server as a known spammer.
By sending bulk email through one of these free providers, you’re likely to end up in the spam folder. But with a dedicated provider like Sendinblue, the email servers have the necessary infrastructure to deliver large volumes of email to the inbox.
And because we maintain strict control over all of our shared IP addresses, users can benefit from excellent deliverability for both marketing emails and transactional emails.
SPF, DKIM and DMARC signatures are managed through our Sendinblue domain names to avoid any DNS issues being flagged by the recipient mail server.
For even more control over your sender reputation, high-volume senders can purchase a dedicated IP address. This way you don’t have to worry about the sending behavior of anyone else affecting your deliverability.
How to choose the best SMTP server to suit your needs
There’s a huge choice of dedicated SMTP sending services on the market. If you’re trying to find the best SMTP service for your business, here are some factors to take into consideration:
- Email volume needs: How much email are you sending? How fast is your business growing? Ideally, you want a solution that can grow with you — without breaking the bank as your needs increase.
- Pricing: What’s your email budget? How do the prices of different solutions compare for the email volume you need?
- Features: What additional features do you need or would be useful to have? Email delivery reports are a must but don’t get distracted by unnecessary bells and whistles.
- Support: As it’s a technical subject, what support options are offered? Do you have an in-house developer to configure the setup? SMTP servers can become more complex as a business grows so it’s good to know what support resources are available.
What’s the best SMTP service for sending bulk email?
We’re biased so of course we’re going to say Sendinblue. But don’t take our word for it. Read these in-depth comparisons with other providers Mailgun and Sendgrid to see how we compare on pricing and features.
How Sendinblue works as a third-party SMTP server
As well as being an email marketing software, Sendinblue also functions as a third party SMTP server. Our users have the option of sending email through us rather than through a webmail client or their own server.
There are number of advantages to using Sendinblue SMTP relay service:
- Quick and easy set up. Once you open your free Sendinblue account all you need to do is activate SMTP. This’ll give you your SMTP credentials to enter into the email client or third party application.
- Benefit from advanced email deliverability and an established sender reputation
- Real-time delivery rates and email performance metrics
- Dedicated IPs for high-volume senders
Can I test Sendinblue’s SMTP server for free?
Yes, you can test Sendinblue’s SMTP email service on the free plan with up to 300 emails a day.
Our free plan also gives access to our email marketing platform, automation, transactional email API, and custom-built email plugins for WordPress and ecommerce platforms.
Pricing for paid plans starts at $25 for 20,000 emails per month and you can store unlimited subscribers at no extra cost.
How to set up Sendinblue’s SMTP relay for sending bulk emails
To send transactional messages from third party web apps and websites over Sendinblue’s SMTP relay, you need to follow these simple steps:
- Open your free Sendinblue account
- Add and authenticate your domain in the Senders and IPs section
- Request the SMTP activation by contacting our support team, specifying whether it’s for marketing or transactional emails
Once SMTP is activated, you’ll be given a set of SMTP credentials.
These credentials can be found by clicking on the company name at the top right of your Sendinblue account and selecting ‘SMTP & API’. SMTP credentials consist of the sending server, a port, login, and password like in the screenshot below.

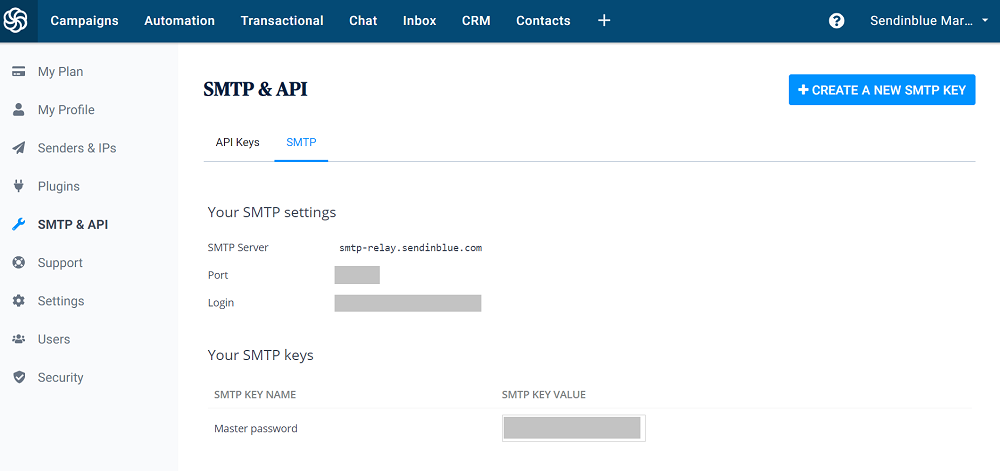
Once you have these details, you’re good to go! Just enter the credentials into the SMTP settings of your email client or other software.
When sending an email, your email client will verify with our server that the SMTP credentials used for authentication are linked to an active Sendinblue account before sending the email on towards the recipient’s mail server.
The easiest way to modify WordPress SMTP settings is with a plugin.
How to set up SMTP email on WordPress
The easiest way to modify WordPress SMTP settings is with a plugin. We recommend our custom-developed WordPress email plugin (or a third party plugin like WP Mail SMTP).
By default, WordPress sends email over the web host’s servers using the wp_mail() function. ISPs often treat email via PHP as suspicious which can lead to the issue of WordPress not sending email to the inbox.
Sendinblue’s SMTP plugin override the defaut WordPress email settings to automatically send email over Sendinblue SMTP. All it takes is a few simple clicks, no coding required.
- Create a Sendinblue account following the steps outlined above.
- Install and activate the Sendinblue plugin on WordPress. Click ‘Sendinblue’ on your WordPress dashboard to configure the settings. Follow Step 2 which requires entering an API key.

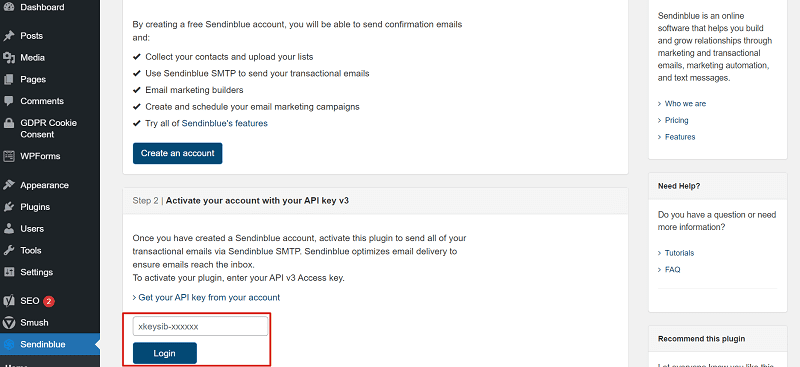
3. Head back over to the Sendinblue dashboard. You’ll find your API key under SMTP & API.


4. Copy and paste the API into the entry field on the plugin dashboard and hit ‘Login‘.
On the next page you’ll be presented with a number of additional settings.
Under transactional emails, select ‘Yes‘ to send WordPress email over Sendinblue SMTP. This will override the default wp_mail() function to automatically use Sendinblue.

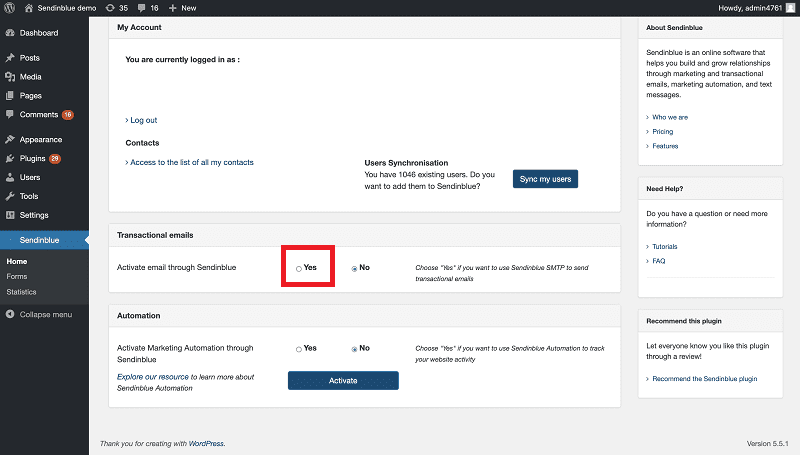
Once these settings are configured, sent a test email via your WordPress contact form. The email should arrive promptly at the destination mailbox as per the contact form settings.
Wrap up
We hope you’ve now got a better understanding of what is SMTP, how an SMTP server works, and why it’s a good idea to invest in a professional SMTP service for sending bulk email.
Any questions, just leave us a comment below.
In the meantime, here’s some other content you might be interested in:
 Deutsch
Deutsch




















Comments
Nice article and explanation. I’m currently using the smtp of http://www.smtpboxes.com with SendBlaster as a smtp client and it works perfect. Anyways that 9k mails per month from sendinblue intrigued me 🙂
Hi Stephen — glad to hear you found our explanation helpful! Feel free to try Sendinblue for free anytime! We’re waiting for you 😉
Such a great article about smtp server. This article is very informative for everyone. Thanks for Sharing.
Ready to find your marketing zen?
Take the stress out of your work day with a solution that’s built for you!
Get started free